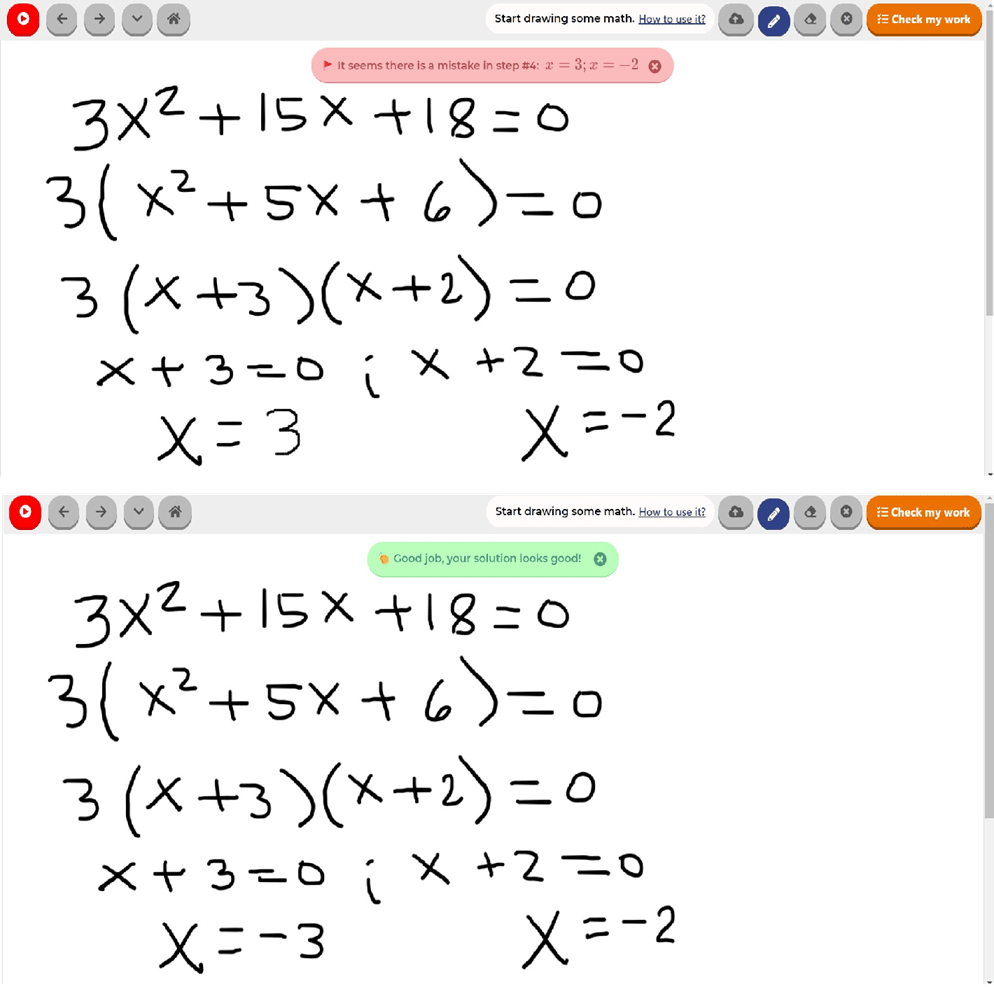
How should I solve this problem?
- Choose an option
- Solve for x
- Solve for y
- Find the derivative using the definition
- Find the derivative using the product rule
- Find the derivative using the quotient rule
- Find the derivative using logarithmic differentiation
- Find the derivative
- Integrate by partial fractions
- Product of Binomials with Common Term
- Load more...